近日,我校食品科技学院食品与纳米技术实验室曾晓雄教授团队在农林科学SCI一区Top期刊《Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry》最新一期(2020, Volume 68, Number 40, pp11128-11143)发表题为《Ascorbic Acid Derivative 2-O-b-D-Glucopyranosyl-L-Ascorbic Acid from the Fruit of Lycium barbarum Modulates Microbiota in the Small Intestine and Colon and Exerts an Immunomodulatory Effect on Cyclophosphamide-Treated BALB/c Mice》(DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c04253)的封面论文。该论文第一作者为食品科技学院2020届本科生黄凯寅,通讯作者为食品科技学院曾晓雄教授和国家枸杞工程中心曹有龙研究员,南京农业大学为第一署名单位。该论文是曾晓雄教授团队在《Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry》上发表的第30篇论文和第3篇封面论文。

近年来越来越多的文献报道肠道是一个强大而独立的免疫系统,其中肠道菌群的组成和结构与人体健康关系十分密切,并且饮食干预可以显著影响肠道菌群的组成和功能。枸杞作为药食同源食物富含多种营养和生物活性物质,具有抗氧化、抗炎症、降血糖等多种生物活性。2-O-b-D-葡萄糖基-L-抗坏血酸(AA-2bG)是一种近年来从枸杞中分离出的天然且稳定的抗坏血酸衍生物,该团队前期研究发现AA-2bG可以缓解葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎,并显著改善结肠炎模型小鼠的肠道菌群结构(Huang et al., 2019);此外,该团队还进一步对长期摄入AA-2bG对正常小鼠肠道菌群的调节进行了探究(Dong et al., 2020)。
本研究采用环磷酰胺(Cy)诱导免疫抑制小鼠模型对AA-2bG的免疫调节作用及其潜在机制进行研究,研究发现AA-2bG可以显著改善Cy引起的机体基本免疫指标变化;同时AA-2bG可以调节小鼠小肠和结肠菌群的结构和组成,显著逆转Cy造成的Proteobacteria、Muribaculaceae等微生物相对丰度的改变。
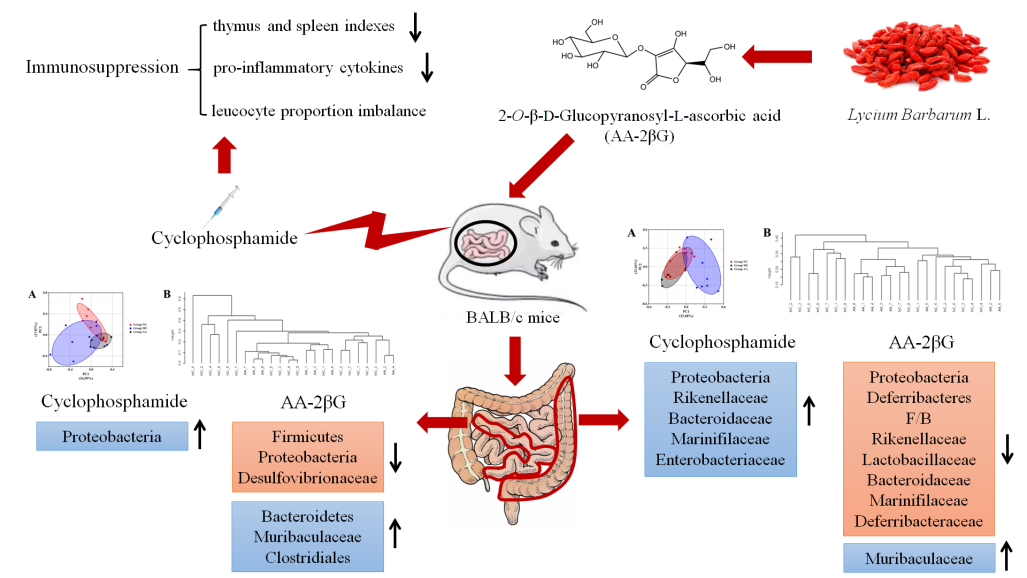
该研究是首个关于AA-2bG免疫调节活性的相关报道,为AA-2bG以及枸杞的药理作用和生物活性提供新的理论支持。该研究工作得到宁夏回族自治区重点科研开发项目(2019BFG02026)、江苏高校优势学科建设工程项目、南京农业大学本科生科研训练(SRT)项目(1818C01)的资助。
原文发表网址:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c04253。
相关论文:
Huang, K.; Dong, W.; Liu, W.; Yan, Y.; Wan, P.; Peng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Cao, Y., 2-O-b-D-Glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid, an ascorbic acid derivative isolated from the fruits of Lycium barbarum L., modulates gut microbiota and palliates colitis in dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2019, 67 (41), 11408-11419. (Cover)
Dong, W.; Huang, K.; Yan, Y.; Wan, P.; Peng, Y.; Zeng, X.; Cao, Y., Long-term consumption of 2-O-b-D-glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid modulate gut microbiota in C57BL/6 mice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020, 68 (33), 8863-8874.
Huang, K.; Yan, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, W.; Zeng, X.; Cao, Y., Ascorbic acid derivative 2-O-b-D-glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid from the fruit of Lycium barbarum modulates microbiota in the small intestine and colon and exerts an immunomodulatory effect on cyclophosphamide-treated BALB/c mice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020, 68 (40), 11128-11143. (Cover)

